Discover How This Innovative System Of IV Fluids Can Transform Your Daily Life
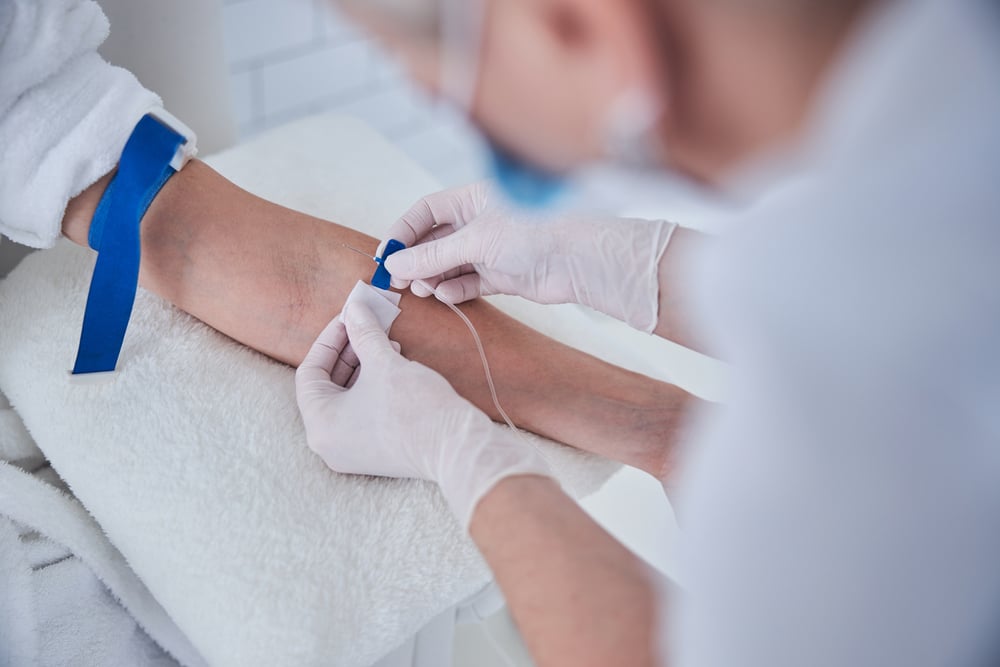
Have you ever seen someone in a hospital hooked up to a clear bag that seems to be magically dripping into their arm? That’s an IV, short for intravenous, a lifeline delivering fluids straight into the bloodstream. For those of us navigating health challenges, understanding what IV fluids are, how they function in our bodies, and who relies on them can really demystify that hospital experience. Whether you’re curious about this process or prepping for a hospital visit, this guide will break down everything you need to know about those seemingly mysterious bags and tubes.
What Are IV Fluids?
IV fluids, or intravenous fluids, are sterile liquids administered directly into a person’s veins through a small catheter and tubing. Think of them as the body’s quick hydration solution—ideal for replenishing lost fluids or delivering medications to those who may not be able to take them orally. Common examples include normal saline (saltwater), dextrose (a sugar solution), and Ringer’s lactate (a balanced mix of fluids and electrolytes that closely mimics blood plasma).
Each type of IV fluid serves a specific purpose tailored to what your body needs at that moment. Because they enter the bloodstream directly, they work much faster than anything you might drink. This is why IV fluids are a staple in emergency rooms, surgical recovery, and urgent care clinics, used for conditions ranging from dehydration to infections to injuries.
How IV Fluids Work
When administered, IV fluids flow straight into your bloodstream through a vein, allowing for almost immediate absorption. Once circulating, these fluids help balance electrolytes like sodium and potassium—crucial components that allow your nerves, muscles, and cells to function optimally. If you’re dehydrated or have lost fluids due to illness or injury, your body might struggle to keep essential organs working efficiently. That’s where IV fluids step in to help.
Whether they’re replenishing lost fluids, assisting in temperature regulation, or flushing out toxins, the impact of IV therapy is fast and precise. It’s one of the reasons why learning the ins and outs of IV therapy is important in nurse practitioner programs and clinical training.
Benefits Of IV Fluids
One of the standout advantages of IV fluids is how quickly they can kick in. When someone is feeling faint or dehydrated, these fluids can restore balance in no time. They’re critical for stabilizing blood pressure during surgeries or when someone is in shock. Plus, the electrolytes in the fluids ensure that your muscles, including the all-important heart, can function properly.
IVs can also deliver medication or nutrition directly into the bloodstream, skipping the digestive processes. This is especially transformative for patients who may be vomiting, unconscious, or simply too weak to eat or drink. In settings like sports medicine, travel clinics, and hospitals, intravenous fluids can accelerate recovery and help individuals avoid potential health crises.
Who Might Need IV Fluids?
A diverse range of individuals may find themselves needing IV fluids. If you’ve been experiencing vomiting, diarrhea, or not drinking enough water, IV hydration can quickly help restore lost fluids. Surgical patients typically receive IV fluids to maintain bodily stability before, during, and after procedures. Infected patients may require both fluids and antibiotics to bolster their immune systems in the fight against illness.
Trauma patients—those injured in car accidents, for example—often need immediate IV intervention. Children and older adults are particularly susceptible to dehydration and may benefit from IV therapy in certain circumstances. Even athletes and long-distance travelers might rely on IV fluids to recover from jet lag or intense physical exertion.
Types Of IV Fluids
When we talk about IV fluids, they primarily break down into two categories: crystalloids and colloids. Crystalloids, which include saline and Ringer’s lactate, are the most commonly administered fluids. These are basically water infused with small dissolved molecules that flow easily through your bloodstream and into your tissues. On the other hand, colloids consist of larger molecules, like proteins or starches, which stay in the bloodstream longer and help draw fluid into the blood vessels.
Colloids are often reserved for situations where someone has low blood volume yet needs to avoid fluid overload. Generally speaking, crystalloids are the first choice for most patients, thanks to their practicality, affordability, and ease of management.
Are There Any Risks?
While IV fluids are generally safe and effective, it’s important to be aware of potential risks and side effects. Common issues might include swelling at the injection site, especially if the IV isn’t placed correctly, or, in rare situations, an infection developing.
Electrolyte imbalances can arise if too much or too little of a specific fluid is given, which could lead to complications down the line. For this reason, healthcare professionals closely monitor patients during IV therapy, trained to pick up on any issues early and make necessary adjustments.
IV fluids represent a straightforward but crucial tool in modern medicine. They hydrate, heal, and support your body when you need a little extra help. If you’re feeling unwell, recovering from surgery, or simply fatigued, IV fluids might be just what you need. They’re widely recognized as safe, effective, and a routine part of care in hospitals and clinics around the globe. If you’re ever unsure about whether you need IV fluids, don’t hesitate to reach out to your healthcare provider—they’re there to guide you every step of the way.